Mexico Tariffs on India: A Deep Dive into Impacts, Motives, and the Future of Bilateral Trade
In recent years, Mexico’s decision to revise and reintroduce tariffs on a number of imported goods—especially those originating from countries with which it does not have a trade agreement—has prompted global discussion. India, being one of the world’s fastest-growing exporters, naturally falls under this policy’s radar.
This article provides a 2000-word, deeply analyzed, human-written explanation of why Mexico imposed tariffs, how these tariffs affect India, which sectors are impacted the most, and what the future holds for India–Mexico trade relations.
• Mexico reintroduced tariffs on several countries, including India, to protect local industries and stabilize its domestic market.
• Indian exports affected include steel, chemicals, engineering goods, pharmaceuticals, auto parts, and textiles.
• Despite tariffs, India–Mexico trade remains strong due to complementary markets and large consumer bases.
• The future depends on negotiations, supply-chain restructuring, and deeper economic engagement.
1. Understanding the Background: Why Mexico Adjusted Its Tariff Policy
Mexico’s tariff structure has historically been shaped by its deep integration with North American supply chains and its extensive network of free trade agreements (FTAs). More than 90% of Mexico’s total trade occurs with countries with which it has formal trade agreements—most importantly the United States and Canada under USMCA (formerly NAFTA).
However, for countries without FTAs, such as India, Mexico has periodically adjusted tariffs to:
- Protect domestic industries from low-cost imports
- Prevent market flooding of cheaper goods
- Support local manufacturing and employment
- Reduce dependency on Asian imports
- Strengthen political ties with trade partners having formal agreements
These tariff changes are not directed specifically at India but apply broadly to several global exporters. India, due to its strong presence in chemicals, steel, machinery, pharmaceuticals, and auto components, naturally gets affected.
2. India–Mexico Trade Relationship: A Growing Strategic Partnership
India and Mexico share a strong diplomatic and economic relationship that has expanded significantly over the last decade. India is one of Mexico’s largest trading partners in Asia, and trade between the two nations has steadily grown across sectors such as energy, automobiles, pharmaceuticals, IT services, and agriculture.
The relationship is supported by strong private sector participation and increasing cross-investments. However, the lack of a formal Free Trade Agreement means tariff barriers remain the biggest challenge.
Key Features of India–Mexico Trade
- Mexico is India’s biggest trading partner in Latin America after Brazil.
- Indian automobile and pharmaceutical companies have a large footprint in Mexico.
- Mexico exports crude oil, machinery, and electronics to India.
- Merchandise trade between the two countries has consistently increased.
This background highlights why tariff adjustments gain immediate attention—they influence major industries on both sides.
3. What Triggered Mexico’s Tariffs Impacting India?
Mexico’s tariff decisions were shaped by a combination of domestic economic considerations and global market pressures. Several key factors are believed to have influenced the policy:
- Influx of competitively priced goods from Asia affecting Mexican domestic production.
- Need to stabilize local industries in the face of global competition.
- Pressure to align policies with USMCA commitments and North American supply chain norms.
- Currency fluctuations that made imports cheaper.
- Mexico’s interest in strategic trade balancing with NAFTA/USMCA partners.
Although India is not the specific target, several Indian export categories fall under Mexico’s tariff-sensitive list.
4. Sectors of Indian Exports Most Affected by Mexico’s Tariffs
The tariff impact varies sector by sector, but Indian industries that export heavily to Mexico have felt the effects more prominently.
| Indian Sector | Impact Level | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Steel & Metals | High | Mexico aims to protect domestic steel makers |
| Chemicals | Moderate | Regulations & safety standards add extra layers |
| Pharmaceuticals | Low–Moderate | High demand keeps trade active despite tariffs |
| Automobile Components | High | NAFTA/USMCA rules favor regional suppliers |
| Textiles | Moderate | Mexico promotes local garment factories |
| IT Hardware | Moderate–High | Logistics + tariff costs influence pricing |
 Why Some Sectors Are More Impacted
Why Some Sectors Are More Impacted
Mexico’s industrial sector—especially automotive and steel—relies on close integration with U.S. industries. Because India competes strongly in these areas with cost-effective production, Mexican policymakers see tariffs as a protective tool.
5. Economic Impact on India: Short-Term & Long-Term Effects
The immediate effect of Mexico’s tariffs is an increase in landed cost for Indian goods, making them slightly less competitive compared to nations with FTAs.
Short-Term Effects
- Higher export costs for Indian manufacturers
- Possible decline in order volumes from Mexican partners
- Shift towards alternative markets in Latin America like Brazil or Chile
- Increased paperwork and compliance requirements
Long-Term Effects
- India may seek a formal trade negotiation with Mexico or a Latin-American bloc.
- Indian companies might set up local manufacturing or assembly plants in Mexico.
- Supply chains may be redesigned to reduce tariff exposure.
- Greater investment from Indian MNCs into Mexican industrial parks.
While tariffs create friction, they also open doors for structural economic adjustments that benefit both nations.
6. Impact on Mexico: Domestic Gains and Economic Challenges
Mexico’s tariff adjustments are designed to strengthen local producers, but the policy has mixed effects:
Positive Outcomes for Mexico
- Protection for domestic industries, especially steel and auto parts
- Motivation for local companies to increase production
- Reduced dependency on Asian imports
- Boost to employment in certain sectors
Challenges Faced by Mexico
- Higher prices for local consumers
- Reduced competitiveness for industries relying on imported inputs
- Potential diplomatic pressure from affected countries
- Risk of supply chain disruptions
Mexico must therefore balance domestic protectionism with international trade commitments.
Also Read:Nobel Prize 2025 Winners List: Names, Achievements
7. Could India and Mexico Move Toward a Trade Agreement?
One of the most frequently discussed possibilities is whether India and Mexico might eventually pursue an FTA or at least a preferential trade agreement.
Given India’s growing presence in the global supply chain and Mexico’s efforts to reduce overdependence on North America, collaboration seems logical.
Potential Benefits of an India–Mexico Trade Pact
- Tariff reduction on Indian goods
- Lower input costs for Mexican manufacturers
- Access to India’s pharmaceutical and IT sectors
- Opportunity for India in Latin American markets via Mexico
However, negotiations in such areas typically take years due to political and economic sensitivities.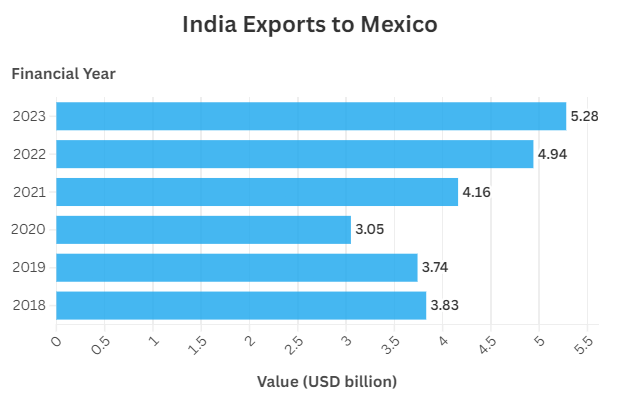
8. How Indian Businesses Are Adapting
Indian exporters and industry bodies have already begun adjusting strategies to handle tariff-related costs. Their responses include:
- Exploring joint ventures with Mexican firms
- Considering manufacturing hubs inside Mexico
- Using third-country routes where tariff conditions differ
- Strengthening market research in Latin America
- Enhancing product differentiation to justify higher pricing
These adaptations help maintain India’s presence in the Mexican market despite tariff challenges.
9. Geopolitical Context: How Global Trends Influence Mexico’s Tariffs
Global politics plays an essential role in shaping tariff decisions. The U.S.–China trade war, changing global alliances, and the rise of Asian exports all influence Mexico’s trade strategies.
Being part of the USMCA bloc, Mexico often finds itself adjusting policies to align with U.S. supply chain objectives. This means countries like India—which are outside the North American ecosystem—face tariff disadvantages unless they build deeper ties with Mexico.
10. Future Outlook: What Lies Ahead for India and Mexico?
While tariffs present short-term challenges, the long-term outlook for India–Mexico trade remains optimistic. Both countries are fast-growing economies with young populations, industrial capability, and global influence.
Future Expectations
- India may negotiate trade concessions in specific sectors
- Mexican industries may demand greater access to the Indian market
- Bilateral dialogues could expand to cover investment, technology, and renewable energy
- Companies from both sides may strengthen partnerships
Ultimately, tariffs represent just one chapter in a broader economic relationship. The appetite for collaboration between India and Mexico is strong, and both nations stand to gain significantly from deeper economic engagement.
Conclusion
Mexico’s tariffs on imports from non-FTA countries—including India—are primarily aimed at protecting domestic industries and balancing global trade pressures. For India, these tariffs create temporary obstacles but also open opportunities for diversification, investment, and innovative partnerships.
With strong economic fundamentals and complementary strengths, India and Mexico are well-positioned to deepen cooperation, explore trade agreements, and build a resilient, mutually beneficial trade relationship in the years ahead.
The story of tariffs is not the end—it is the beginning of the next phase of India–Mexico economic evolution.
Also Read:Dhurandhar Movie Review (2025): रणवीर सिंह की Powerful वापसी या सिर्फ एक और एक्सपेरिमेंट?


You must be logged in to post a comment.